Frequently Asked Questions
What is Share Price?
A share price, interchangeably used with a stock price, represents the current market value of one share of a publicly listed company. Essentially, it’s the amount you pay to buy one share of a company’s equity on a stock market or the money you receive when you sell it.
What am I buying by buying one share?
When you buy one share of a listed company on a stock market, you’re acquiring a small ownership stake in that company. As a shareholder, you gain specific rights and benefits, such as voting rights for electing the board of directors and receiving dividends in proportion to your shareholding. Importantly, as a shareholder, your liability is limited to the amount you’ve invested, offering protection against losses beyond your initial investment.
What is Market Capitalization (MCap) and how can we calculate it?
Market capitalization is the total market value of a company’s equity, calculated by multiplying the share price of the company (market price of a share) by the outstanding number of shares. The outstanding number of shares represents all the shares that a company has issued.
Why Market Cap is important?
Understanding market capitalization is crucial for investors as it helps in creating investment strategies based on the size of companies. Investors seeking higher growth potential often focus on mid-cap or smaller companies, which are predominantly listed on the Iraq Stock Exchange. Moreover, investors can analyze competing companies within the same industry or sector based on Mcap to identify market leaders and those experiencing faster growth. This can be done by comparing current market capitalizations and the growth rates in market capitalizations of these companies.
How is the initial value of shares determined?
In the stock market, listed companies (those trading on the stock market) have varying share prices. Understanding why their share prices differ is crucial for understanding the stock market. Knowing how share prices are determined also enhances your ability to make informed investment decisions
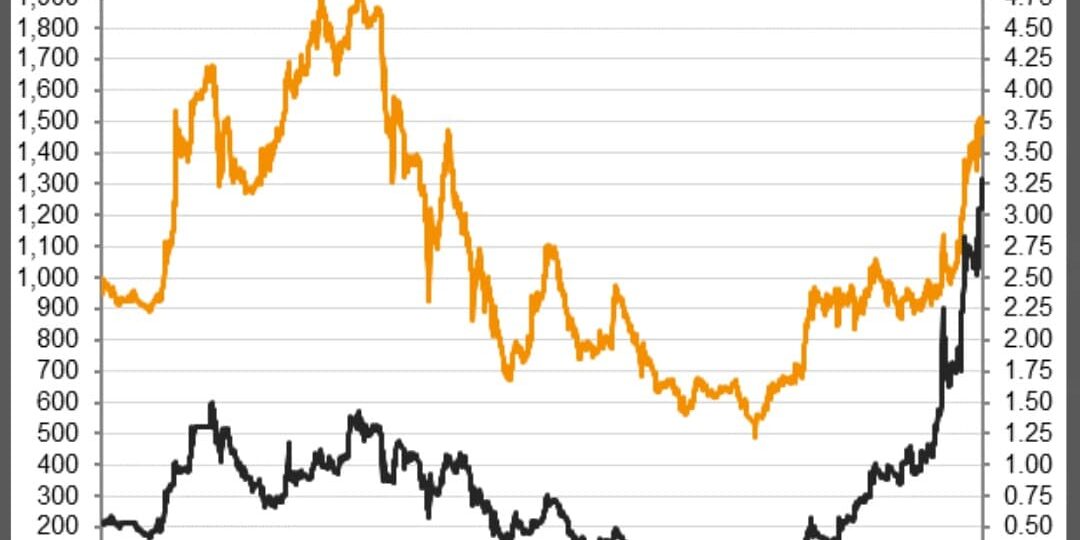
How is a Share Price Determined daily in the market?
Following the listing, the share price is continuously determined by occurring trades, influenced by various factors. For a trade to be executed, investors wanting to buy shares at a certain price must be matched with other investors wanting to sell shares at that price.
Which factors affect the share prices?
Share prices are influenced by various factors, including the company’s financial performance, market conditions, investor sentiment, and overall economic trends. These factors collectively shape supply and demand dynamics in the market, which in turn impact share prices. When demand for a stock exceeds supply, causing more investors to want to buy than sell, the share price typically rises. Conversely, if there are more sellers than buyers, leading to an excess of supply over demand, the share price tends to fall. Other factors affecting the share price include but are not limited to; political developments, industry trends, company news (such as investments or legal issues) and corporate actions (like rights issue, bonus issue, dividend distributions).